guarding system
Links
R
Links

R
In choosing the right oil seal type for your application, it is essential to assess factors such as speed, temperature range, pressure levels, chemical compatibility, shaft material, and installation space limitations. By considering these factors carefully, you can ensure that you select an oil seal that will provide optimal performance and longevity in your specific application.
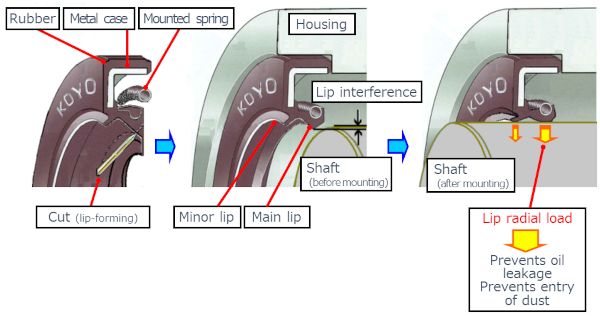
These seals are more commonly used in pumps, motors both electric & hydraulic, gearboxes & occasionally dirt wipers in hydraulic cylinders. They help protect shafts and bearings from dirt and harmful contaminants entering the internals of the application that they are fitted to, as well as prevent any leaks of lubricant.
Orient your seal the same way as the initial install.The sealing lip should face the lubricant that requires sealing.The second lip on a double lip oil seal is intended as a dust lip. The seal must be installed at a 90°, or perpendicularly, to both the shaft and housing bore. This is an issue in cases where the housing does not have a counterbore or shoulder the seal can seat up against.

Here are some additional tips that will help you have a successful O-ring installation.
For more detailed information, please see the following:
There is a British Standard laid down for the control of synthetic rubbers. BS 3574 (1989) helps to determine shelf life – for instance, Nitrile (NBR) and Polyacrylic (ACM) are Group ‘B’ rubbers and have a 7-year life, whilst Silicone (VMQ) and Fluoroelastomers (Viton®) are Group ‘C’ rubbers and have a 10-year shelf life. PTFE and Leather do not come into this category but like the others should be kept in the original packing for as long as possible away from direct light, dust, and humidity. Ozone, which can also be produced by battery-driven forklift trucks has a very bad effect on synthetic rubbers. Finally, protect the sealing lip – DO NOT hang the seals on nails, wire etc.
Note how the mounting nuts or bolts are fitted, then undo them. Have ready some wooden wedges to use as supports, and a strong helper to hold the engine steady.
Similar to the housing surface stop technique, this method uses a stop at the machined housing face to set the seal depth. It is typically used in housings with flat outer surfaces. Verifying the placement through visual inspection or with a feeler gauge ensures placement accuracy.