loading...
- No. 9, Xingyuan South Street, Dongwaihuan Road, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui, Hebei, China
- admin@zjcomposites.com
- +86 15097380338
- Welcome to visit our website!
structural frp fiberglass
Understanding Structural FRP Fiberglass Applications, Benefits, and Future Prospects
Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP), particularly fiberglass, has emerged as a significant material in various structural applications. Due to its unique properties, including high corrosion resistance, low weight, and impressive tensile strength, fiberglass is becoming a preferred choice in construction, infrastructure, and even aerospace industries. This article delves into the aspects of structural FRP fiberglass, exploring its applications, benefits, and future prospects.
What is FRP Fiberglass?
FRP fiberglass is composed of a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers. The glass fibers provide the material with remarkable strength and stiffness, while the polymer matrix offers protection against environmental degradation. This combination results in a composite that not only behaves well mechanically but also withstands the rigors of various environmental conditions. FRP comes in many forms, including sheets, rods, and reinforcements, making it versatile for numerous applications.
Applications of Structural FRP Fiberglass
1. Construction and Infrastructure One of the most notable applications of FRP fiberglass is in construction. It is regularly used for beams, columns, and decks, primarily in situations where traditional materials like steel or concrete may not perform optimally. For instance, bridges and walkways can benefit from lightweight FRP components that reduce the overall load on supporting structures. Furthermore, its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for projects in marine environments, such as piers or coastal structures.
2. Transportation The aerospace and automotive industries are also significant users of fiberglass. In aerospace, FRP is utilized in making lightweight fuselage components, enhancing fuel efficiency while maintaining structural integrity. Similarly, in the automotive sector, fiberglass is employed in manufacturing body panels and components that contribute to weight reduction without sacrificing safety.
3. Energy Sector The energy industry has embraced structural FRP fiberglass for wind turbine blades. The lightweight and robust nature of fiberglass allows for longer blades, which can capture more wind energy while remaining structurally sound. Additionally, FRP composite materials are increasingly used in the construction of chemical storage tanks and piping systems due to their resistance to harsh chemicals and environmental conditions.
4. Sports and Recreation Sporting goods often incorporate FRP fiberglass owing to its lightweight and strong properties. Items such as fishing rods, bicycles, and kayaks are frequently made from this material, benefitting from both performance and durability in demanding conditions.
structural frp fiberglass
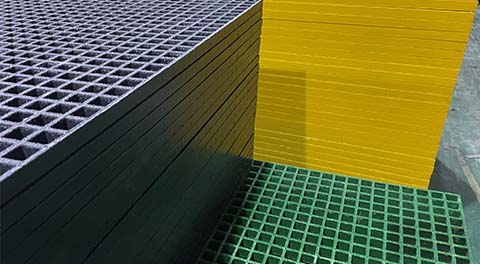
Benefits of Structural FRP Fiberglass
The benefits of using FRP fiberglass in structural applications are numerous
- Low Weight to Strength Ratio FRP fiberglass is significantly lighter than traditional materials like steel or concrete, leading to lower shipping and handling costs. - Corrosion Resistance Unlike metals, fiberglass does not corrode over time, which reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of the structures. - Design Flexibility The composite can be molded into complex shapes to meet specific design requirements, offering architects and engineers greater creativity. - Thermal and Electrical Insulation FRP fiberglass is non-conductive and provides excellent thermal insulation, making it suitable for various environments.
Future Prospects
As environmental issues and sustainability become increasingly significant, the demand for eco-friendly building materials is rising. FRP fiberglass, with its recyclable nature (in some forms) and longevity, presents an attractive option for sustainable construction. Moreover, ongoing research aims to improve the properties of FRP composites, potentially leading to enhanced performance and reduced costs.
Advancements in manufacturing processes, such as automated pultrusion and resin infusion techniques, promise to enhance the scalability and efficiency of FRP fiberglass production. As these technologies evolve, it’s likely that structural fiberglass will become more prevalent across a myriad of applications, making a compelling case for its adoption in modern engineering and architectural projects.
Conclusion
Structural FRP fiberglass stands at the forefront of composite material technology, demonstrating immense potential across various industries. Its versatility, durability, and resistance to environmental challenges make it a go-to solution for many applications, from construction and transportation to energy production. As research and development continue to drive innovation in this field, the future of FRP fiberglass looks bright, promising even broader applications and enhanced performance.
-
The Rise of FRP Profiles: Strong, Lightweight, and Built to LastNewsJul.14,2025
-
SMC Panel Tanks: A Modern Water Storage Solution for All EnvironmentsNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Grating: A Modern Solution for Safe and Durable Access SystemsNewsJul.14,2025
-
Galvanized Steel Water Tanks: Durable, Reliable, and Ready for UseNewsJul.14,2025
-
FRP Mini Mesh Grating: The Safer, Smarter Flooring SolutionNewsJul.14,2025
-
Exploring FRP Vessels: Durable Solutions for Modern Fluid HandlingNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Structures: The Future of Lightweight, High-Performance EngineeringNewsJun.20,2025
