loading...
- No. 9, Xingyuan South Street, Dongwaihuan Road, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui, Hebei, China
- admin@zjcomposites.com
- +86 15097380338
- Welcome to visit our website!
water treatment systems
Water Treatment Systems Ensuring Clean and Safe Water
Water is an essential resource for life, and ensuring its quality is crucial for both human health and environmental sustainability. Water treatment systems play a vital role in purifying water by removing contaminants and making it safe for consumption and use. These systems vary widely in terms of technology, scale, and application, but they all share a common goal to provide clean water.
One of the primary types of water treatment systems is the conventional treatment process, often found in municipal water treatment plants. This process typically involves several stages including coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection. Coagulation involves adding chemicals to the water to bind contaminants together into larger particles called floc. These particles then settle at the bottom of a sedimentation tank. Afterward, filtration removes remaining impurities, and disinfection – often using chlorine or ultraviolet light – ensures that any pathogenic microorganisms are eradicated. This method is reliable and widely used, but it requires significant infrastructure and operational expertise.
For smaller communities or rural areas lacking conventional facilities, decentralized water treatment systems are a practical alternative. These systems can range from simple sand filters to more advanced membrane filtration technologies. Decentralized systems are scalable, making them suitable for various settings, and they often require less investment than large municipal plants. However, they still necessitate proper maintenance and oversight to ensure water quality meets safety standards.
water treatment systems
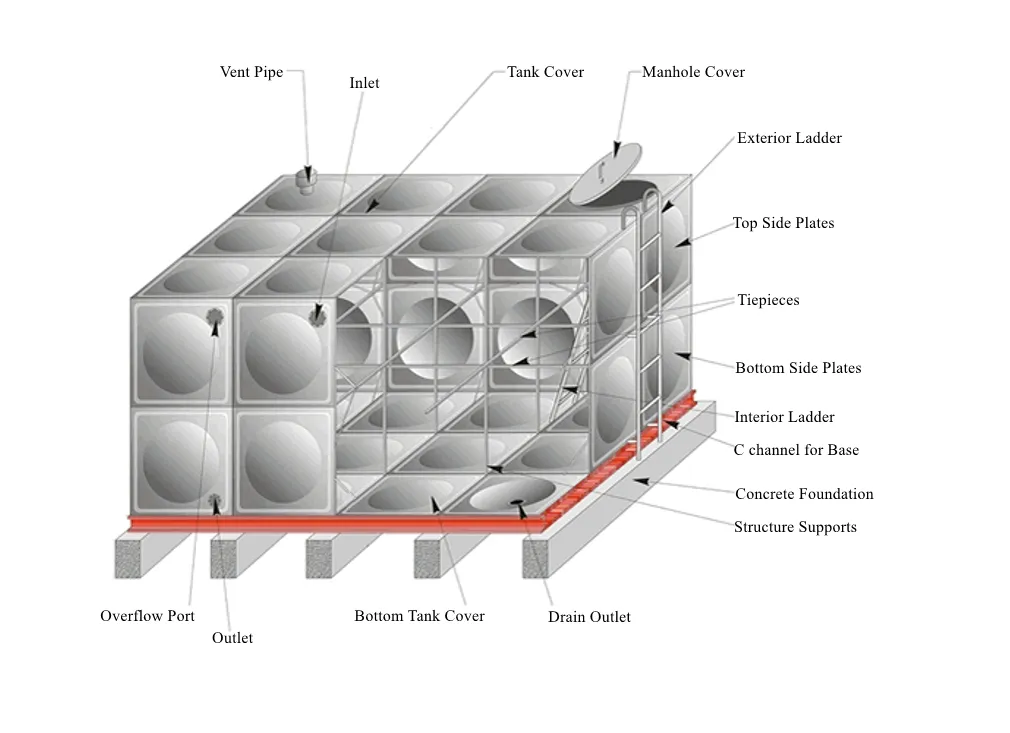
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in advanced treatment technologies. These include reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, and advanced oxidation processes. Reverse osmosis, for example, is highly effective at removing a wide range of contaminants, including salts, heavy metals, and even some microorganisms. These technologies are particularly beneficial in areas facing water scarcity or high levels of pollution, as they can produce high-quality water from brackish or severely contaminated sources.
Despite advancements in technology, water treatment systems must also address the challenges posed by emerging contaminants such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and endocrine disruptors. Traditional treatment methods may not effectively remove these substances, leading to concerns about long-term health impacts. As a result, researchers and engineers are continually seeking innovative solutions to enhance the effectiveness of water treatment systems in dealing with these complex pollutants.
Moreover, water treatment systems must be sustainable and energy-efficient. The push towards more eco-friendly practices is leading to the development of systems that minimize energy usage and waste generation. For example, integrated water resource management emphasizes the reuse of treated wastewater for non-potable applications, thereby conserving fresh water supplies and reducing the strain on existing sources.
In summary, water treatment systems are crucial for safeguarding public health and the environment. As technology evolves, these systems must continue to adapt to new challenges and incorporate sustainable practices. By investing in innovative and efficient water treatment solutions, we can ensure access to clean and safe water for current and future generations.
-
The Rise of FRP Profiles: Strong, Lightweight, and Built to LastNewsJul.14,2025
-
SMC Panel Tanks: A Modern Water Storage Solution for All EnvironmentsNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Grating: A Modern Solution for Safe and Durable Access SystemsNewsJul.14,2025
-
Galvanized Steel Water Tanks: Durable, Reliable, and Ready for UseNewsJul.14,2025
-
FRP Mini Mesh Grating: The Safer, Smarter Flooring SolutionNewsJul.14,2025
-
Exploring FRP Vessels: Durable Solutions for Modern Fluid HandlingNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Structures: The Future of Lightweight, High-Performance EngineeringNewsJun.20,2025
