loading...
- No. 9, Xingyuan South Street, Dongwaihuan Road, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui, Hebei, China
- admin@zjcomposites.com
- +86 15097380338
- Welcome to visit our website!
Exploring Group Structures and Their Implications in Various Mathematical Contexts
Understanding GRP Structures An Overview
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) structures have revolutionized the construction and manufacturing industries, offering remarkable benefits that traditional materials cannot match. This article will explore the nature of GRP structures, their advantages, applications, and environmental considerations, providing a comprehensive overview of this modern material.
What Are GRP Structures?
GRP, also known as fiberglass, is a composite material made by embedding glass fibers in a resin matrix. This combination creates a lightweight, strong, and durable material that can be molded into various shapes and sizes. The versatility of GRP allows it to be used in a wide range of applications, from construction to automotive manufacturing.
One of the defining characteristics of GRP is its excellent resistance to corrosion and weathering. Unlike metals, which can rust or corrode when exposed to moisture and chemicals, GRP maintains its structural integrity over time, making it an ideal choice for outdoor applications. Moreover, GRP structures can be produced in a variety of colors and finishes, increasing their aesthetic appeal.
Advantages of GRP Structures
1. Lightweight One of the primary advantages of GRP is its light weight compared to traditional materials like steel or concrete. This attribute simplifies transportation and installation, reducing overall project costs.
2. Strength and Durability GRP structures possess high tensile strength and can withstand significant loads without deforming. Even under extreme conditions, such as high winds or heavy precipitation, GRP components maintain their structural integrity.
3. Corrosion Resistance As mentioned earlier, GRP does not corrode when exposed to moisture or chemicals. This quality makes it suitable for industries such as wastewater treatment, chemical processing, and marine applications, where materials are constantly subject to harsh environments.
4. Insulation GRP has excellent thermal insulation properties, making it a favorable option for applications requiring temperature control. This characteristic also contributes to energy efficiency.
grp structures
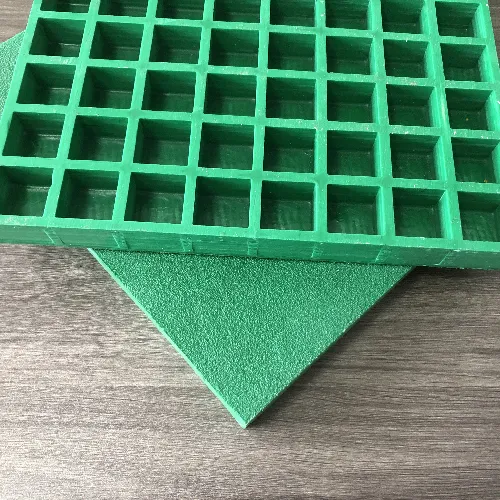
5. Design Flexibility The manufacturing process for GRP allows for high levels of customization. Structures can be created in various shapes, sizes, and colors, accommodating specific design requirements and aesthetic preferences.
Applications of GRP Structures
The versatility of GRP has led to its adoption across various sectors
- Construction GRP is widely used in constructing roofs, facades, and cladding. Its lightweight nature reduces the load on supporting structures, making it an excellent choice for modern architecture.
- Transportation In the automotive and aerospace industries, GRP is utilized to manufacture components such as body panels, interiors, and other structural elements where weight reduction is critical for performance and fuel efficiency.
- Marine The marine industry employs GRP for boat hulls, decks, and other components due to its corrosion resistance, which prolongs the lifespan of vessels in saltwater environments.
- Industrial Applications GRP is often found in manufacturing facilities for components such as storage tanks, ducting systems, and process equipment, providing durability in environments where traditional materials may fail.
Environmental Considerations
While GRP offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider its environmental impact. The production of GRP involves the use of synthetic resins, which can have a carbon footprint. However, advancements in recycling technologies are helping mitigate some of these concerns. Companies are increasingly focusing on developing bio-based resins and finding ways to recycle GRP materials at the end of their service life.
In summary, GRP structures represent a significant advancement in material science and engineering. Their combination of lightweight properties, strength, durability, and design flexibility opens up a world of possibilities across various industries. As technology continues to advance and more sustainable practices are adopted in GRP production, it is reasonable to expect that the applications and benefits of this versatile material will continue to expand. The future of construction and manufacturing is being reshaped by the innovative use of GRP structures, affirming their place as an essential component in the modern materials landscape.
-
The Rise of FRP Profiles: Strong, Lightweight, and Built to LastNewsJul.14,2025
-
SMC Panel Tanks: A Modern Water Storage Solution for All EnvironmentsNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Grating: A Modern Solution for Safe and Durable Access SystemsNewsJul.14,2025
-
Galvanized Steel Water Tanks: Durable, Reliable, and Ready for UseNewsJul.14,2025
-
FRP Mini Mesh Grating: The Safer, Smarter Flooring SolutionNewsJul.14,2025
-
Exploring FRP Vessels: Durable Solutions for Modern Fluid HandlingNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Structures: The Future of Lightweight, High-Performance EngineeringNewsJun.20,2025
