loading...
- No. 9, Xingyuan South Street, Dongwaihuan Road, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui, Hebei, China
- admin@zjcomposites.com
- +86 15097380338
- Welcome to visit our website!
frp vessel with multiport valve
FRP Vessels with Multiport Valves A Comprehensive Overview
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) vessels have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their remarkable properties, such as corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and high strength-to-weight ratio. One of the critical components that enhance the functionality of these vessels is the multiport valve. This article will explore the significance of FRP vessels equipped with multiport valves, their workings, applications, and advantages.
What are FRP Vessels?
FRP vessels are composite structures made of polymer resins reinforced with fiberglass. These vessels can be designed for a variety of applications, including chemical storage, water treatment, and various industrial processes. The inherent characteristics of FRP, such as resistance to harsh chemicals and environmental conditions, make these vessels ideal for storing corrosive substances that would otherwise deteriorate traditional materials, like metals.
The Role of Multiport Valves
Multiport valves are versatile devices that allow the control of fluid flow from a single source to multiple outlets. These valves play a pivotal role in optimizing the operation of FRP vessels. Typically, a multiport valve has several ports (or opening points) that enable it to switch the direction of flow, thereby controlling the distribution of liquids or gases in and out of the vessel.
The design of these valves is crucial; they are engineered to maintain flow integrity and minimize pressure loss while providing a reliable way to manage fluids. This is particularly important in processes where precision is key, such as in chemical reactions, filtration processes, or any scenario requiring the movement of aggressive fluids.
Applications of FRP Vessels with Multiport Valves
The combination of FRP vessels and multiport valves finds applications across various sectors, including
1. Chemical Processing In chemical plants, FRP vessels store corrosive chemicals, while multiport valves help manage the flow to and from reactors, separators, and other processes.
2. Water Treatment FRP vessels are used in filtration systems, where multiport valves control the backwashing and flow of water through different treatment stages.
frp vessel with multiport valve
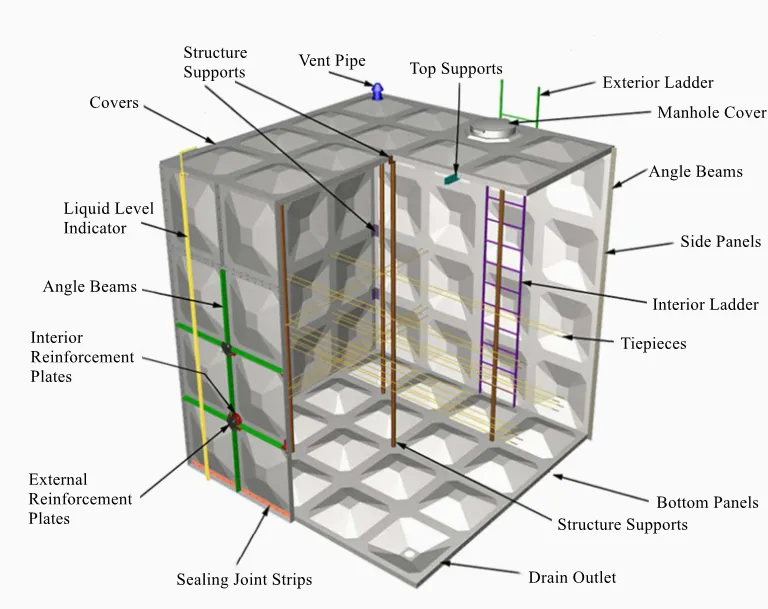
4. Pharmaceuticals The pharmaceutical industry requires strict adherence to hygiene and chemical compatibility, making FRP vessels with multiport valves suitable for storing and processing reactive substances.
Advantages of Using FRP Vessels with Multiport Valves
1. Corrosion Resistance The combination of FRP and multiport valves effectively manages a wide range of corrosive materials. This reduces the risk of leaks and failures that can arise from traditional metal vessels.
2. Lightweight and Durable FRP vessels are significantly lighter than metal counterparts, facilitating easier transportation and installation. Coupled with the robustness of multiport valves, this makes for an efficient material handling solution.
3. Cost-Effectiveness While the initial investment might be higher, the longevity and reduced maintenance requirements for FRP vessels and multiport valves can lead to long-term cost savings.
4. Versatility Multiport valves offer flexibility in operation. They can be configured to suit various processes, allowing industries to adapt more rapidly to changing operational needs.
5. Ease of Maintenance FRP vessels often require less frequent maintenance compared to traditional vessels. Multiport valves, with their straightforward design, also simplify maintenance tasks without requiring special tools.
Conclusion
The integration of FRP vessels with multiport valves represents a significant advancement in fluid management systems across various industries. Their combined advantages — corrosion resistance, lightweight design, and operational versatility — make them ideal for handling a wide range of chemicals and processes. As industries continue to seek more efficient and resilient solutions, it is likely that the use of FRP vessels equipped with multiport valves will expand, driving innovation and improving operational efficiency in numerous applications. By understanding the unique benefits and functionalities of these systems, companies can better position themselves to tackle the challenges of modern industrial processes.
-
The Rise of FRP Profiles: Strong, Lightweight, and Built to LastNewsJul.14,2025
-
SMC Panel Tanks: A Modern Water Storage Solution for All EnvironmentsNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Grating: A Modern Solution for Safe and Durable Access SystemsNewsJul.14,2025
-
Galvanized Steel Water Tanks: Durable, Reliable, and Ready for UseNewsJul.14,2025
-
FRP Mini Mesh Grating: The Safer, Smarter Flooring SolutionNewsJul.14,2025
-
Exploring FRP Vessels: Durable Solutions for Modern Fluid HandlingNewsJul.14,2025
-
GRP Structures: The Future of Lightweight, High-Performance EngineeringNewsJun.20,2025
