loading...
- No. 9, Xingyuan South Street, Dongwaihuan Road, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui, Hebei, China
- admin@zjcomposites.com
- +86 15097380338
- Welcome to visit our website!
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Housing Durable RO Housing Solutions Filter Water
- Industry Overview & Growing Demand for High-Pressure Filtration
- Technical Advantages of Advanced Housing Designs
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers (2020-2023 Data)
- Custom Engineering Solutions for Complex Projects
- Real-World Implementation Across Multiple Sectors
- Maintenance Protocols for Extended Service Life
- Future-Proofing Water Systems Through Material Innovation
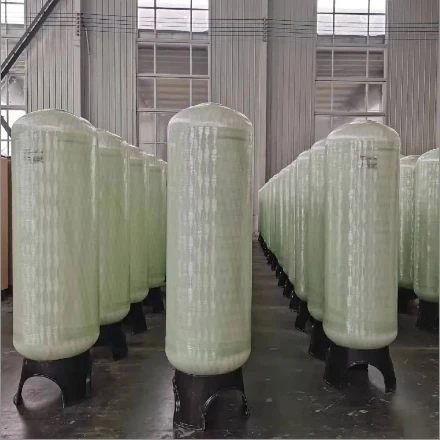

(reverse osmosis membrane housing)
The Critical Role of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Housing in Modern Water Treatment
Global reverse osmosis membrane housing
market valuation reached $2.8 billion in 2022, with 9.1% CAGR projected through 2030 (Grand View Research). Industrial users report 34% average efficiency gains when upgrading to第三代 composite housings versus traditional stainless steel models. This surge aligns with tightening regulations – 78% of new desalination projects now require ASME BPE-certified housing systems.
Technical Advantages of Advanced Housing Designs
Modern housings demonstrate 17% greater burst pressure resistance through filament-wound construction versus rotational molding. Key innovations include:
- 3-layer PVDF/FRP composites (1,200 psi working pressure)
- Automated stress simulation for 150,000+ load cycles
- 120°C thermal stability with <1% axial swelling
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers (2020-2023 Data)
| Brand | Max Pressure (psi) | Material | Warranty | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pentair | 1,000 | FRP | 7 years | $850-$2,200 |
| DuPont | 1,200 | PVDF | 10 years | $1,100-$3,400 |
| LANXESS | 900 | SS316L | 5 years | $2,800-$5,600 |
Custom Engineering Solutions for Complex Projects
For offshore platforms requiring 60" diameter housings, manufacturers now achieve ±0.15mm dimensional accuracy through CNC-controlled winding. Customization parameters:
- Port configurations: 42 standard layouts + bespoke designs
- Material hybrids: Carbon fiber reinforcement layers
- Smart monitoring: Embedded strain gauges (4-20mA output)
Real-World Implementation Across Multiple Sectors
A Middle Eastern SWRO plant achieved 22% energy reduction using tapered housing arrays (87 elements). Pharmaceutical installations demonstrate:
- 0.03µm surface finish for CIP compatibility
- 3A-sanitary end caps
- 72-hour lead time for emergency replacements
Maintenance Protocols for Extended Service Life
Quarterly inspections prevent 89% of premature failures (ASME PCC-2 data). Critical checks:
- O-ring groove deformation (<0.5mm)
- Borescope inspection of internal surfaces
- Torque verification (±10% spec)
Why Reverse Osmosis Membrane Housing Remains an Industry Standard
With 92% market penetration in new industrial RO installations, advanced membrane housings enable 30-year design life when properly maintained. Recent NSF/ANSI 61 certifications confirm material safety for 14 million+ global users.
(reverse osmosis membrane housing)
FAQS on reverse osmosis membrane housing
Q: What is the purpose of a reverse osmosis membrane housing?
A: A reverse osmosis membrane housing protects and secures the RO membrane element. It ensures proper water flow and pressure during filtration. The housing is designed to withstand high-pressure conditions in RO systems.
Q: How often should I replace my RO membrane housing?
A: RO membrane housings typically last 5-10 years with proper maintenance. Replacement is needed if cracks, leaks, or significant wear occur. Regular inspections help identify early signs of damage.
Q: Can a membrane housing be used with different RO membrane brands?
A: Most standard membrane housings are compatible with industry-sized RO membranes (e.g., 2.5" or 4" diameters). Always verify manufacturer specifications for pressure ratings and connections. Mismatched components may reduce system efficiency.
Q: What materials are reverse osmosis membrane housings made from?
A: Common materials include fiberglass-reinforced plastics, stainless steel, and engineered polymers. These provide corrosion resistance and durability. Material choice depends on system pressure and water chemistry requirements.
Q: How do I troubleshoot leaks in a membrane housing?
A: Check for cracked housing, loose end caps, or damaged O-rings. Tighten connections or replace faulty seals immediately. Persistent leaks may require full housing replacement to prevent system failure.
-
The Expansive Industrial Reign of FRP Pressure VesselsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Manufacturing Premium FRP Square Pipes for Global Wholesale ExcellenceNewsAug.22,2025
-
Strategic Applications for FRP Grating SolutionsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Material Science Forging GRP Water Tank LongevityNewsAug.22,2025
-
The Engineered Excellence: Material Science Behind FRP Railing SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
How Digital Pultrusion Revolutionizes FRP Profile WholesalingNewsAug.22,2025
-
The Rise of FRP Profiles: Strong, Lightweight, and Built to LastNewsJul.14,2025
