loading...
- No. 9, Xingyuan South Street, Dongwaihuan Road, Zaoqiang County, Hengshui, Hebei, China
- admin@zjcomposites.com
- +86 15097380338
- Welcome to visit our website!
The Engineered Excellence: Material Science Behind FRP Railing Systems
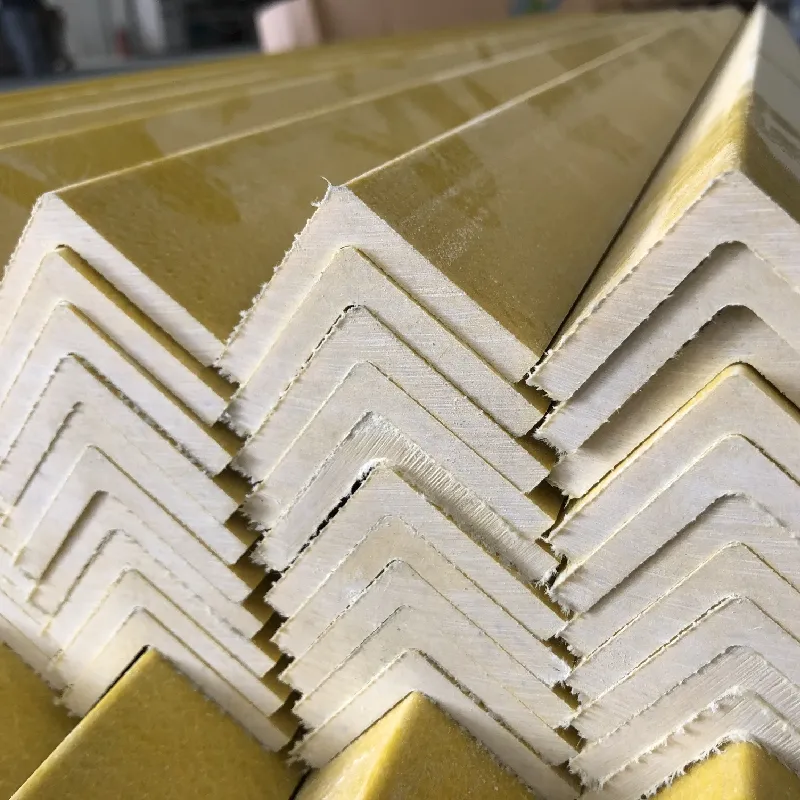
The construction and industrial sectors increasingly demand solutions that combine durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness, especially for critical safety components like railings, handrails, and guardrails. Enter Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP). Moving beyond traditional materials like wood, steel, or aluminum, FRP offers a compelling alternative, particularly in harsh environments where corrosion, weight, and maintenance are major concerns. Understanding the material composition and manufacturing processes is key to appreciating why FRP railings and FRP guardrails excel in demanding wholesale applications. This deep dive explores the science and technology that make these systems reliable, long-lasting assets for large-scale projects.
Demystifying the FRP Railings Matrix: Core Components of Strength
At its heart, FRP is a composite material, meaning it combines two or more distinct constituents to create a product superior to its individual parts. The performance of FRP handrails and FRP guardrails hinges on this synergistic relationship:
- The Reinforcing Fiber: The Backbone of Strength:This is the primary load-bearing element. Glass fiber (fiberglass) is the most common and cost-effective choice for railings, providing excellent tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility. For specialized, ultra-high-performance applications, carbon fiber or aramid fibers might be used, offering exceptional stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios, though at significantly higher cost. The fibers are typically woven into mats, rovings (bundles), or fabrics, dictating directional strength properties.
- The Polymer Resin: The Protective Binder:This matrix binds the fibers together, transfers loads between them, protects them from environmental damage, and provides the shape and surface finish. The resin choice dramatically impacts the final product's properties:
- Polyester Resins:Economical and widely used. Offer good chemical resistance and mechanical properties. Suitable for many standard FRP handrail and guardrail applications.
- Vinyl Ester Resins:Superior corrosion resistance compared to polyester, particularly against acids, alkalis, and solvents. Excellent moisture resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for FRP guardrails in aggressive environments like chemical plants, wastewater facilities, and marine settings. They bridge the gap between polyester and epoxy in performance and cost.
- Epoxy Resins:Offer the highest mechanical strength, adhesion, and chemical/thermal resistance. Often used in high-performance or critical structural applications, though typically more expensive than vinyl ester or polyester. Less common in standard railing profiles but vital for specialized components or connections.
- Additives and Fillers: Tailoring Performance:A range of additives is incorporated to enhance specific characteristics:
- Pigments:Provide consistent, integral color throughout the profile, eliminating the need for painting.
UV Inhibitors/Stabilizers: Crucial for exterior FRP railing systems to prevent resin degradation and color fading from sunlight exposure.
- Fire Retardants:Added to meet specific fire safety codes for building materials.
- Fillers:Can be used to modify viscosity, reduce cost, or enhance specific properties like fire resistance or surface smoothness.
- Surface Veils:Thin layers of fine fiber (often polyester or glass) applied to the mold surface first, creating a smooth, resin-rich outer layer that enhances corrosion resistance and provides a better cosmetic finish for FRP handrails.
This carefully engineered combination results in a material inherently resistant to corrosion, rot, insects, and UV degradation, while being lightweight yet incredibly strong – the perfect foundation for long-lasting safety systems.
Crafting the Form: Key Manufacturing Processes for FRP Railings
Transforming the raw materials into the precise shapes required for FRP railings, FRP handrails, and FRP guardrails involves sophisticated manufacturing techniques. The choice of process significantly influences production volume, cost, dimensional consistency, and final properties:
- Pultrusion: The Champion of Consistency & Volume:This is the dominant process for producing straight, constant-cross-section profiles like top rails, handrail bodies, posts, and pickets – essentially the core structural elements of FRP railing systems.
- Open Molding: Flexibility for Complex Shapes:Used for creating complex geometries, large panels, curved sections, fittings (elbows, bases, end caps), and custom infill panels that might be part of a FRP guardrailsystem.
- Closed Molding (RTM/Vacuum Infusion): Enhanced Quality for Demanding Parts:Processes like Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Vacuum Infusion offer improved quality control and higher fiber content than open molding for critical or high-performance components.
- Advantages for Wholesale:Produces parts with excellent surface finish on both sides, higher and more consistent mechanical properties due to controlled resin ratios and reduced voids, good for complex shapes requiring high strength or cosmetic quality, suitable for medium-volume production runs of specialized FRP handrail fittings or custom guardrail sections.
- Fabrication & Assembly:Regardless of the primary shaping process, components often require secondary fabrication: cutting to precise lengths, drilling mounting holes, and assembling profiles into complete FRP railingsections using specialized FRP adhesives and mechanical fasteners designed for the material.
For wholesale suppliers, pultrusion offers the efficiency and consistency needed for large-scale projects, while other processes provide the flexibility to meet specific design requirements within those projects.
FAQ: About FRP Railing Systems
What are the primary advantages of FRP railings over steel or aluminum?
The core advantages are exceptional corrosion resistance (immune to rust and rot), significantly lighter weight (easier handling and installation, reduced structural load), very low maintenance (no painting or galvanizing required), non-conductive (electrical safety), inherent UV resistance (with proper resins/coatings), and long-term durability in harsh environments. This translates to lower lifecycle costs despite a potentially higher initial material cost.
How durable are FRP handrails in extreme weather and UV exposure?
Properly formulated FRP handrails are highly durable. The use of isophthalic or vinyl ester resins, coupled with integral UV inhibitors in the gel coat and resin matrix, provides excellent resistance to weathering, UV degradation, and temperature extremes. They won't warp, crack, splinter, or corrode like traditional materials, maintaining structural integrity and appearance for decades, even in coastal or high-sun environments.
What manufacturing process ensures FRP railing the highest consistency for wholesale volumes?
Pultrusion is the gold standard for high-volume, consistent production of straight FRP railing profiles (top rails, posts, mid-rails). It produces parts with uniform cross-sections, excellent dimensional accuracy, high fiber content for strength, and a smooth finish, batch after batch. This consistency is crucial for wholesalers supplying large projects where parts must fit together perfectly.
Are FRP guardrails compliant with building and safety codes?
Yes, reputable manufacturers design and test their FRP guardrail systems to meet or exceed relevant building codes and safety standards. This includes requirements for height, load-bearing capacity (top rail and infill), deflection limits under load, and graspability specifications for handrails. Wholesalers should provide documentation confirming compliance for specific product lines.
What are the key considerations for wholesalers stocking FRP railing systems?
Key considerations include: Supplier Quality & Consistency (rigorous manufacturing controls), Material Specifications (resin type - vinyl ester preferred for harsh environments, UV protection level), Compliance Documentation (code approvals, load test reports), Range & Compatibility, Packaging & Logistics (optimized for bulk transport without damage), and Technical Support. Focusing on high-performance vinyl ester systems often offers the best balance for demanding wholesale applications.
The science behind FRP railings, FRP handrails, and FRP guardrails reveals why they are not just an alternative, but often the superior choice for modern infrastructure. The deliberate selection of high-strength fibers embedded in corrosion-resistant polymer matrices, shaped through precise manufacturing like pultrusion, creates safety systems built to last where others fail. The benefits – unwavering corrosion resistance, minimal maintenance, lightweight ease, inherent safety, and long-term durability – translate directly into significant value for wholesalers and their clients, especially when considering total project lifecycle costs.
-
Revolutionizing Industrial Safety with ZJ Composites' Mini Mesh GratingNewsNov.14,2025
-
Premium FRP Profiles and FRP Grating Revolution for Global WholesalersNewsNov.14,2025
-
Ultimate Strength with ZJ Composites FRP Profiles for Wholesale SuccessNewsNov.14,2025
-
ZJ Composites Covered Grating – The Durable Flooring Solution for Smarter Industrial SpacesNewsNov.14,2025
-
Mini Mesh Grating Enhancing Strength and Style in Every ProjectNewsNov.14,2025
-
FRP Pressure Vessels by ZJ CompositesNewsNov.14,2025
-
Transforming Industrial Spaces with Advanced Frp GratingNewsNov.11,2025